Supported files
File sources
There are two types of embroidery file format:
| Design: | Design files, also known as ‘outline’ or 'all-in-one' files usually contain digitized shapes and lines, selected stitch types and stitch values and effects. |
| Machine: | Machine files, also known as ‘stitch’ files contain only stitches and machine functions and are suited to specific embroidery machines. |
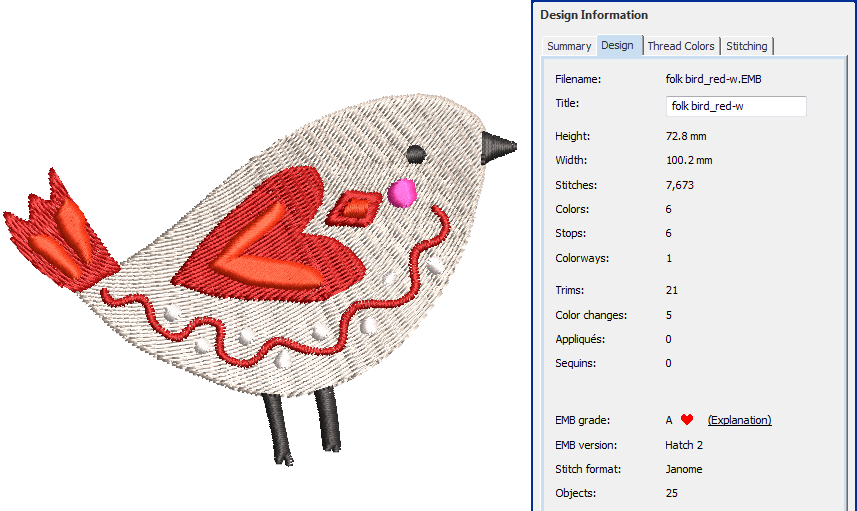
While design files are broadly classified as ‘embroidery’ (outline) or ‘machine’ (stitch), the software internally tags files as belonging to one of four types – native design (A), imported outlines (B), processed stitches (C), or imported stitches (D). These are summarized as follows:
| Grade | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | Native design | Native EMB designs as well as ART and JAN files are all ‘Grade A’ design formats read and written by the software. They are called ‘Grade A’ because they contain a complete set of design information in a single file – object outlines, properties, stitches, thread colors, thumbnail image, and comments. It goes without saying that only Grade A files provide 100% perfect scaling and transformation. |
| B | Imported outlines | Designs read from an outline format such as CND / GNC and saved in ART / EMB / JAN format. Such designs cannot be read directly by the software but once converted, they are treated as Grade B designs. |
| C | Processed stitches | Designs read from machine files – EXP, DST, PES, etc – where stitches have been converted to objects. Such converted files may have limitations in resizing. |
| D | Imported stitches | Designs read from stitch files, where outlines may or may not have been recognized, but stitches have not been regenerated through stitch processing. Note, however, that if you change a stitch design – e.g. add a lettering object – the status changes to ‘Processed Stitches’ even though the imported stitches may not have been regenerated. Such files are not generally suited to resizing. |
For information about the source of an embroidery file, refer to the Design tab of the Design Information docker.